-
Modeling Strategic Objectives and Behavior in the Transition of the Energy Sector to Inform Policymaking
in The Electricity Journal
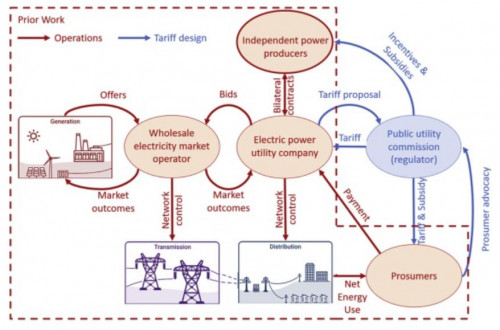
The typical starting point and centerpiece of energy decarbonization is the electric power sector, a large direct GHG emitter. Published in The Electricity Journal, this paper explores what the modeling community should do to inform this transition, including expanding energy market datasets and designing models that incorporate multiple objectives and manifold actors behaving strategically in a framework consisting of large uncertainty, while accounting for the physics of power systems.
-
Toward Rationality in Oil and Gas Leasing
Building the Toolkit for Programmatic Reforms
Leasing public lands and waters for fossil-fuel extraction drives a quarter of U.S. carbon dioxide emissions. Our new report offers analytic tools for federal leasing decisions to drive policies that maximize economic and environmental welfare—nationally and locally.
-
Regulating Risk from Toxic Substances
Best Practices for Economic Analysis of Risk Management Options Under the Toxic Substances Control Act
This report identifies best practices EPA should adopt to holistically assess and weigh the costs and benefits of risk management options, allowing the agency to meet its statutory obligations and best enhance public welfare.
-
Climate and Power System Reliability in the Aftermath of the Texas Blackouts
The February 2021 blackout in Texas underscored the importance of reliable and resilient power systems. This article discusses the roles of regulators, markets, fuel and generation supply chains, and interdependent infrastructures, and finds that they need to be reconsidered and redefined to successfully meet the future challenges of increased electrification and severe weather
-
Playing with Fire
Responding to Criticism of the Social Cost of Greenhouse Gases
Federal agencies will need to offer considered and detailed responses to objections raised in the notice-and-comment processes for individual regulations or administrative actions that apply the Working Group’s social cost valuations. Given its expertise, the Working Group should consider providing such responses now, so that agencies can then incorporate them into future actions. This working paper offers a blueprint for those responses.
-
Expert Elicitation and the Social Cost of Greenhouse Gases
The Interagency Working Group on the Social Cost of Greenhouse Gases can use the findings from expert elicitations to improve the U.S. federal government’s social cost of greenhouse gas estimates, which are used in regulatory cost-benefit analysis and other policy contexts. Our report highlights several component updates, incorporating data from expert elicitations, that the Working Group should consider during its current update of the social cost of greenhouse gas estimates.
-
About Time
Recalibrating the Discount Rate for the Social Cost of Greenhouse Gases (Working Paper)
In light of recent evidence, a new range of discount rates appropriate for calculating the social cost of greenhouse gases could be conservatively estimated as between 0.5%-2.5%, with a central estimate of 1.5%. Agencies should follow the Interagency Working Group’s guidance on applying new social cost of greenhouse gas estimates based on updated discount rates—and will need to justify their choices, including any departures from prior practices.
-
Strategically Estimating Climate Pollution Costs in a Global Environment
Debate has reemerged about whether federal agencies’ policy analyses should focus on those climate pollution costs that will occur only within U.S. borders, rather than on the full global valuation of climate damages. The Interagency Working Group on the Social Cost of Greenhouse Gases provides compelling justifications to focus on global estimates. Based on a wide range available evidence, the Working Group should consider recommending a domestic valuation of at least 75% or more of the global values for optional use as a lower-bound estimate in sensitivity analysis.
-
Broadening the Use of the Social Cost of Greenhouse Gases in Federal Policy
Our working paper highlights numerous areas in which the federal government should apply the social cost of greenhouse gases beyond regulatory cost-benefit analysis. It is organized under the framework of “decision-making, budgeting, and procurement” laid out in the President’s executive order, identifying a number of relevant actions—like environmental reviews conducted under NEPA and the assessment of royalty rates for federal land-management. In short, application of the social cost of greenhouse gases would be extremely beneficial for any executive branch decision with significant greenhouse gas implications.
-
Strategic Policymaking for Implementing Renewable Portfolio Standards: A Tri-level Optimization Approach
Forthcoming
Appropriately designed renewable support policies can play a leading role in promoting renewable expansions and contribute to low emission goals. Meanwhile, ill-designed policies may distort electricity markets, put power utilities and generation companies on an unlevel playing field and, in turn, cause inefficiencies. This paper, forthcoming in IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, proposes a framework to optimize policymaking for renewable energy sources, while incorporating conflicting interests and objectives of different stakeholders.
Viewing recent projects in Publications