-

Presidential Transitions: The New Rules
Published in Yale Journal on Regulation
There has been a general assumption that the norm-breaking was a result of the Trump Administration’s lack of respect for the rule of law and that it would subside when a new administration took office. This article challenges this assumption, showing that the Trump-era toolkit on rollbacks has now also been used aggressively—in some cases more aggressively—by the Biden Administration. Actions that might have been seen as an aberration four years ago should now be regarded as integral components of the administrative state.
-

Does Unconventional Energy Extraction Generate More Wastewater? A Lifetime Perspective
Published in Ecological Economics
The paper analyzes how wastewater generation patterns differ between unconventional wells and conventional wells, accounting for differences in well configurations and local geology. Using the 2008–2016 monthly production data from 50,039 wells, the authors show that unconventional wells generated more wastewater in the first 12 months of production but less cumulative discharge than conventional wells. Unconventional oil wells had a lower wastewater-to-energy ratio throughout their lifetime than their conventional counterparts, whereas no efficiency gap existed among gas wells. These findings call for targeted strategies to balance the short-term disposal burden and the long-term efficiency gains of unconventional energy extraction.
-
Costs, Confusion, and Climate Change
Yale Journal on Regulation
Recently, some prominent public policy experts and scholars have proposed that a “marginal abatement cost” (MAC) could be used as an alternative to the social cost of carbon (SCC). This article provides conceptual clarity about these metrics, focusing on how a MAC-based threshold could sensibly be used in climate policy, and explaining why it is not a substitute for the SCC.
-
The Social Cost of Greenhouse Gases: Legal, Economic, and Institutional Perspective
Yale Journal on Regulation
The social cost of greenhouse gases provides the best available method to quantify and monetize incremental climate damages. To date, however, the use of the method for such determinations and processes has been sporadic and fairly limited. Published in the Yale Journal on Regulation, this article evaluates the various legal, economic, and institutional controversies surrounding the social cost of greenhouse gases, and explains why this metric should play a critical role in guiding agency policymaking and decision-making related to climate change.
-
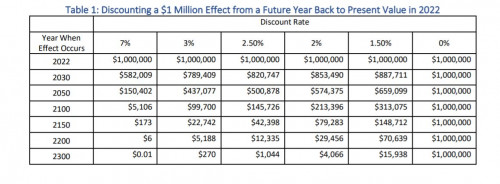
Valuing the Future: Legal and Economic Considerations for Updating Discount Rates
Yale Journal on Regulation
This article explores the legal and economic considerations for updating discount rates and details the compelling economic evidence for lowering the current default rates for regulatory analyses. It argues that a declining discount rate framework can consistently harmonize agency practices and so put agencies on sound legal footing in their approach to valuing the future.
Viewing all publications in Academic Articles/Working Papers