-
Modeling Strategic Objectives and Behavior in the Transition of the Energy Sector to Inform Policymaking
in The Electricity Journal
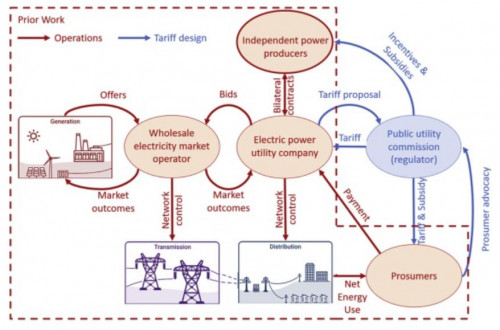
The typical starting point and centerpiece of energy decarbonization is the electric power sector, a large direct GHG emitter. Published in The Electricity Journal, this paper explores what the modeling community should do to inform this transition, including expanding energy market datasets and designing models that incorporate multiple objectives and manifold actors behaving strategically in a framework consisting of large uncertainty, while accounting for the physics of power systems.
-
Climate and Power System Reliability in the Aftermath of the Texas Blackouts
The February 2021 blackout in Texas underscored the importance of reliable and resilient power systems. This article discusses the roles of regulators, markets, fuel and generation supply chains, and interdependent infrastructures, and finds that they need to be reconsidered and redefined to successfully meet the future challenges of increased electrification and severe weather
-
Playing with Fire
Responding to Criticism of the Social Cost of Greenhouse Gases
Federal agencies will need to offer considered and detailed responses to objections raised in the notice-and-comment processes for individual regulations or administrative actions that apply the Working Group’s social cost valuations. Given its expertise, the Working Group should consider providing such responses now, so that agencies can then incorporate them into future actions. This working paper offers a blueprint for those responses.
-
About Time
Recalibrating the Discount Rate for the Social Cost of Greenhouse Gases (Working Paper)
In light of recent evidence, a new range of discount rates appropriate for calculating the social cost of greenhouse gases could be conservatively estimated as between 0.5%-2.5%, with a central estimate of 1.5%. Agencies should follow the Interagency Working Group’s guidance on applying new social cost of greenhouse gas estimates based on updated discount rates—and will need to justify their choices, including any departures from prior practices.
-
Broadening the Use of the Social Cost of Greenhouse Gases in Federal Policy
Our working paper highlights numerous areas in which the federal government should apply the social cost of greenhouse gases beyond regulatory cost-benefit analysis. It is organized under the framework of “decision-making, budgeting, and procurement” laid out in the President’s executive order, identifying a number of relevant actions—like environmental reviews conducted under NEPA and the assessment of royalty rates for federal land-management. In short, application of the social cost of greenhouse gases would be extremely beneficial for any executive branch decision with significant greenhouse gas implications.
Viewing all publications in Academic Articles/Working Papers