-
Measuring the Benefits of Power Plant Effluent Regulation
The 2020 Steam Electric Reconsideration Rule and Potential Future Methods
EPA is considering regulations that would clean up the wastewater discharges from power plants, after they were stalled and then rolled back under the Trump administration. As it conducts that analysis, this report urges EPA to provide a robust assessment of the benefits of the regulation, improving on analysis that was conducted in the Obama era. The report reviews the economic framework, literature, and analyses performed to support both the original Obama-era rule and Trump-era revisions, building on Davis Noll and Rothschild (2021), which detailed numerous impacts of the 2020 Rule that EPA neglected to examine. This review highlights key considerations that will strengthen future regulations.
-
Comments to EPA on Proposed Transport Rule
In April 2022, EPA proposed a Federal Implementation Plan (FIP) to reduce interstate transport of ozone pollution using the Clean Air Act's Good Neighbor Provision. We submitted comments supporting the Proposed FIP and recomming that EPA select the regulatory alternative that maximizes net benefits and revise and expand its distributional analysis to better reflect the impacts of the Proposed FIP on vulnerable groups. We also submitted joint comments with a coalition of environmental groups supporting EPA's use of the social cost of greenhouse gases in the Proposed FIP.
-
Joint Comments to SEC on its Proposal to Enhance and Standardize Climate-Related Disclosures
Together with the Environmental Defense Fund and Professor Madison Condon of Boston University School of Law, we submitted three sets of comments to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in support of its Proposed Rule on the Enhancement and Standardization of Climate-Related Disclosures for Investors (Proposed Rule). The Proposed Rule would require publicly traded companies to disclose important information about the extent to which climate change is already affecting their financial performance, their approach to climate-related risk management, their climate-relevant governance structures, and their greenhouse gas emissions, which serve as a proxy for exposure to risk from policy- and market-driven shifts to a clean-energy economy.
-
Costs, Confusion, and Climate Change
Yale Journal on Regulation
Recently, some prominent public policy experts and scholars have proposed that a “marginal abatement cost” (MAC) could be used as an alternative to the social cost of carbon (SCC). This article provides conceptual clarity about these metrics, focusing on how a MAC-based threshold could sensibly be used in climate policy, and explaining why it is not a substitute for the SCC.
-
The Social Cost of Greenhouse Gases: Legal, Economic, and Institutional Perspective
Yale Journal on Regulation
The social cost of greenhouse gases provides the best available method to quantify and monetize incremental climate damages. To date, however, the use of the method for such determinations and processes has been sporadic and fairly limited. Published in the Yale Journal on Regulation, this article evaluates the various legal, economic, and institutional controversies surrounding the social cost of greenhouse gases, and explains why this metric should play a critical role in guiding agency policymaking and decision-making related to climate change.
-
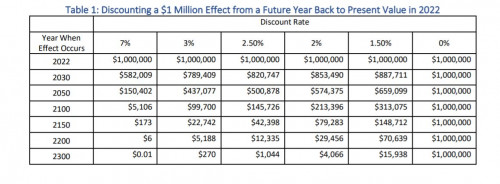
Valuing the Future: Legal and Economic Considerations for Updating Discount Rates
Yale Journal on Regulation
This article explores the legal and economic considerations for updating discount rates and details the compelling economic evidence for lowering the current default rates for regulatory analyses. It argues that a declining discount rate framework can consistently harmonize agency practices and so put agencies on sound legal footing in their approach to valuing the future.
-
Joint SC-GHG Comments on Proposed DOE Standards for Room Air Conditioners and Pool Heaters
Together with partner groups, we submitted joint comments to the Department of Energy (DOE) on its proposed rule to strengthen energy conservation standards for room air conditioners and pool heaters. Our comments applaud the agency for appropriately applying the social cost of greenhouse gases to estimate the climate benefits of the proposed standards, even though the standards would be cost-benefit justified without considering any climate benefits. We also encourage DOE to expand upon its rationale for adopting a global damages valuation and for the range of discount rates it applies to climate effects.
-
Regulating Immortal Accounts
How the FTC Can Limit Unwanted Data Retention
The report argues that an FTC rule requiring reasonable cancellation practices for all market actors and providing clear and specific guidelines would address the harms of immortal accounts. Such regulation would fall under the FTC’s authority and advance the Commission’s mission to protect consumers and competition by preventing deceptive, unfair, and anticompetitive business practices.
-
Comments to EPA on Proposed Heavy-Duty Vehicle Emission Standards
In March 2022, EPA proposed standards to regulate emissions of nitrogen oxides and particulate matter from heavy-duty vehicles beginning with Model Year 2027. Policy Integrity submitted comments recommending that EPA strengthen these crucial standards in order to fulfill EPA's statutory duty to set standards "reflecting the greatest degree of emission reduction achievable." We also made a number of recommendations designed to ensure that EPA is properly comparing regulatory alternatives and accounting for the benefits of strong regulation.
-
Amicus Brief in Fifth Circuit Supporting Reversal of Injunction on the Social Cost of Greenhouse Gases
In this amicus brief, we explain how the Interagency Working Group based its climate-damage valuations on voluminous and expert science, and that its approach followed regulatory guidance and precedent. In particular, the brief supports the Working Group's selection of discount rates and geographic scope, explaining how those choices followed expert consensus and were consistent with agency treatment of other regulatory impacts.